The Penultimate Web Developer’s Cheat Sheet
The Penultimate Web Developer’s Cheat Sheet
I am literally just going to combine a fair number of my Cheat Sheets in no particular order.
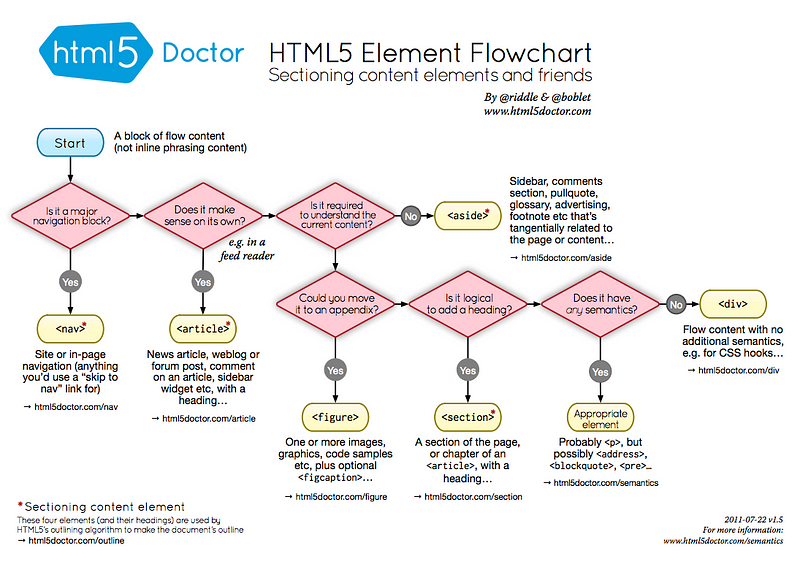
HTML:
<!-- Document Summary -->
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- Tells the browser that HTML5 version of HTML to be recognized by the browser -->
<html lang="en"></html> <!-- The HTML lang attribute is used to identify the language of text content on the web. This information helps search engines return language specific results, -->
<head></head> <!-- Contains Information specific to the page like title, styles and scripts -->
<title></title> <!-- Title for the page that shows up in the browser title bar -->
<body></body> <!-- Content that the user will see -->
<!-- Document Information -->
<base/> <!-- Usefull for specifying relative links in a document -->
<style></style> <!-- Contains styles for the html document -->
<meta/> <!-- Contains additional information about the page, author, page description and other hidden page info -->
<script></script> <!-- Contains all scripts internal or external -->
<link/> <!-- Used to create relationships with external pages and stylesheets -->
<!-- Document Structure -->
<h1></h1> ... <h6></h6> <!-- All six levels of heading with 1 being the most promiment and 6 being the least prominent -->
<p></p> <!-- Used to organize paragraph text -->
<div></div> <!-- A generic container used to denote a page section -->
<span></span> <!-- Inline section or block container used for creating inline style elements -->
<br/> <!-- Creates a line-break -->
<hr> <!-- Creates a sectional break into HTML -->
<!-- Text Formatting -->
<strong></strong> and <b></b> <!-- Makes text contained in the tag as bold -->
<em></em> and <i></i> <!-- Alternative way to make the text contained in the tag as italic -->
<strike></strike> <!-- Creates a strike through the text element -->
<pre></pre> <!-- Preformatted monospace text block with some spacing intact -->
<blockquote></blockquote> <!-- Contains long paragraphs of quotations often cited -->
<abbr></abbr> <!-- Contains abbreviations while also making the full form avaialable -->
<address></address> <!-- Used to display contact information -->
<code></code> <!-- Used to display inline code snippets -->
<q></q> <!-- Defines a short inline quotation -->
<sub></sub> <!-- Defines subscripted text -->
<sup></sup> <!-- Defines superscripted text -->
<kbd></kbd> <!-- Specifies text as keyboard input -->
<small></small> <!-- Specifies small text -->
<!-- Links Formatting -->
<a href="url"></a> <!-- Used to link to external or internal pages of a wbesite -->
<a href="mailto:email@example.com"></a> <!-- Used to link to an email address -->
<a href="name"></a> <!-- Used to link to a document element -->
<a href="#name"></a> <!-- Used to link to specific div element -->
<a href="tel://####-####-##"></a> <!-- Used to display phone numbers and make them clickable -->
<!-- Image Formatting -->
<img src="url" alt="text"> <!-- Used to display images in a webpage where src="url" contains the link to the image source and alt="" contains an alternative text to display when the image is not displayed -->
<!-- List Formatting -->
<ol></ol> <!-- Used to create ordered lists with numbers in the items -->
<ul></ul> <!-- Used to display unordered lists with numbers in the items -->
<li></li> <!-- Contains list items inside ordered and unordered lists -->
<dl></dl> <!-- Contains list item definitions -->
<dt></dt> <!-- Definition of single term inline with body content -->
<dd></dd> <!-- The descrpition of the defined term -->
<!-- Forms Formatting and Attributes -->
<form action="url"></form> <!-- Form element creates a form and action="" specifies where the data is to be sent to when the visitor submits the form -->
<!-- Supported attributes -->
method="somefunction()" <!-- Contains the type of request (GET, POST... etc) which dictates how to send the data of the form -->
enctype="" <!-- Dictates how the data is to be encoded when the data is sent to the web server. -->
autocomplete="" <!-- Specifies if the autocomplete functionality is enabled or not -->
novalidate <!-- Dictates if the form will be validated or not -->
accept-charset="" <!-- Identifies the character encoding upon form submission -->
target="" <!-- Tell where to display the information upon form submission. Possible values: '_blank', '_self', '_parent', '_top' -->
<fieldset disabled="disabled"></fieldset> <!-- Identifies the group of all fields in the form -->
<label for=""></label> <!-- A simple field label telling the user what to type in the field -->
<legend></legend> <!-- The form legend acts as a caption for the fieldset element -->
<input type="text/email/number/color/date"> <!-- Input is the input field where the user can input various types of data -->
<!-- Supported attributes -->
name="" <!-- Describes the name of the form -->
width="" <!-- Specifies the width of an input field -->
value="" <!-- Describes the value of the input information field -->
size="" <!-- Specifies the input element width in characters -->
maxlength="" <!-- Specifies the maximum input character numbers -->
required="" <!-- Specifies if the input field is required to fill in before submitting the form -->
step="" <!-- Identifies the legal number intervals of the input field -->
<textarea name="" id="" cols="30" rows="10"> <!-- Specifies a large input text field for longer messages -->
</textarea>
<select name=""></select> <!-- Describes a dropdown box for users to select from variety of choices -->
<!-- Supported attributes -->
name="" <!-- The name for a dropdown combination box -->
size="" <!-- Specifies the number of available options -->
multiple <!-- Allows for multiple option selections -->
required <!-- Requires that a value is selected before submitting the form -->
autofocus <!-- Specifies that the dropdown automatically comes to focus once the page loads -->
<optgroup></optgroup> <!-- Specifies the entire grouping of available options -->
<option value=""></option> <!-- Defines one of the avaialble option from the dropdown list -->
<button></button> <!-- A clickable button to submit the form -->
<!-- Tables Formatting -->
<table></table> <!-- Defines and contains all table related content -->
<caption></caption> <!-- A description of what table is and what it contains -->
<thead></thead> <!-- The table headers contain the type of information defined in each column underneath -->
<tbody></tbody> <!-- Contains the tables data or information -->
<tfoot></tfoot> <!-- Defines table footer -->
<tr></tr> <!-- Contains the information to be included in a table row -->
<th></th> <!-- Contains the information to be included in a single table header -->
<td></td> <!-- Contains actual information in a table cell -->
<colgroup></colgroup> <!-- Groups a single or multiple columns for formatting purposes -->
<col> <!-- Defines a single column of information inside a table -->
<!-- Objects and iFrames -->
<object data=""></object> <!-- Describes and embed file type including audio, video, PDF's, images -->
<!-- Supported attributes -->
type="" <!-- Describes the type of media embedded -->
height="" <!-- Describes the height of the object in pixels -->
width="" <!-- Describes the width of the object in pixels -->
usemap="" <!-- This is the name of the client-side image map in the object -->
<iframe src="" frameborder="0"></iframe> <!-- Contains an inline frame that allows to embed external information -->
<embed src="" type=""> <!-- Acts as a container for external application or plug-in -->
src="" <!-- The source of the external file you're embedding -->
width="" <!-- Describes the width of the iframe in pixels -->
<!-- HTML5 New Tags -->
<header></header> <!-- Defines the header block for a document or a section -->
<footer></footer> <!-- Defines the footer block for a document or a section -->
<main></main> <!-- Describes the main content of a document -->
<article></article> <!-- Identifies an article inside a document -->
<aside></aside> <!-- Specifies content contained in a document sidebar -->
<section></section> <!-- Defines a section of a document -->
<details></details> <!-- Describes additonal information that user can view or hide -->
<dialog></dialog> <!-- A dialog box or a window -->
<figure></figure> <!-- An independent content block featuring images, diagrams or illustrations -->
<figcaption></figcaption> <!-- Caption that describe a figure -->
<mark></mark> <!-- Displays a portion of highlighted text with in a page content -->
<nav></nav> <!-- Navigation links for the user in a document -->
<menuitem></menuitem> <!-- The specific menu item that a user can raise from a pop up menu -->
<meter></meter> <!-- Describes the scalar measurement with in a known array -->
<progress></progress> <!-- Displays the progress of a task usually a progress bar -->
<rp></rp> <!-- Describes text within the browsers that do not support ruby notations -->
<rt></rt> <!-- Displays east asian typography character details -->
<ruby></ruby> <!-- Describes annotations for east asian typography -->
<summary></summary> <!-- Contains a visible heading for details element -->
<bdi></bdi> <!-- Helps you format parts of text in a different direction than other text -->
<time></time> <!-- Identifies the time and date -->
<wbr> <!-- A line break within the content -->
<!-- Some other useful tags -->
<canvas></canvas> <!-- Allows to draw 2D shapes on the web page with the help of javascript -->
<keygen> <!-- Represents a control for generating a public-private key pair -->
<map></map> <!-- Specifies an image map -->
<!-- Collective Character Obejcts -->
" " Quotation Marks - "
& & Ampersand - &
< < Less than sign - <
> > Greater than sign - >
  Non-breaking space
© © Copyright Symbol - ©
@ Ü @ symbol - @
• ö Small bullet - .
™ û Trademark Symbol - ™


GIT:

CSS:


Bootstrap:

Bash:
Continued:


Python:
- Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose, dynamically typed programming language
- It is also Object oriented, modular oriented and a scripting language.
- In Python, everything is considered as an Object.
- A python file has an extension of .py
- Python follows Indentation to separate code blocks instead of flower brackets({}).
- We can run a python file by the following command in cmd(Windows) or shell(mac/linux).
-
python <filename.py>
By default, the python doesn’t require any imports to run a python file.
Create and execute a program
- Open up a terminal/cmd
- Create the program: nano/cat > nameProgram.py
- Write the program and save it
- python nameProgram.py
Basic Datatypes
![Data TypeDescriptionintInteger values [0, 1, -2, 3]floatFloating point values [0.1, 4.532, -5.092]charCharacters [a, b, @, !, `]strStrings [abc, AbC, A@B, sd!, `asa]boolBoolean Values [True, False]charCharacters [a, b, @, !, `]complexComplex numbers [2+3j, 4–1j]](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*g1SbmDwyQP_-e4jDRkhrpg.png)
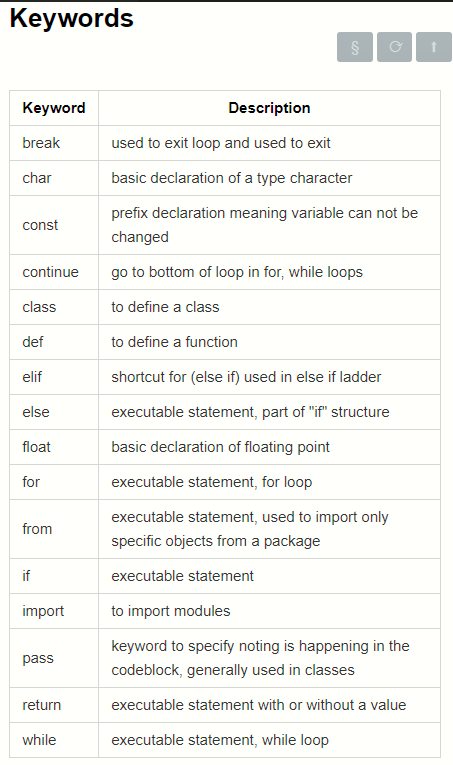
Keywords
Operators
![OperatorDescription( )grouping parenthesis, function call, tuple declaration[ ]array indexing, also declaring lists etc.!relational not, complement, ! a yields true or false~bitwise not, ones complement, ~a-unary minus, — a+unary plus, + a*multiply, a * b/divide, a / b%modulo, a % b+add, a + b-subtract, a — b<<shift left, left operand is shifted left by right operand bits>>shift right, left operand is shifted right by right operand bits<less than, result is true or false, a %lt; b<=less than or](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*WhZHWsF544F3Jou4TOdlvQ.png)
![OperatorDescription( )grouping parenthesis, function call, tuple declaration[ ]array indexing, also declaring lists etc.!relational not, complement, ! a yields true or false~bitwise not, ones complement, ~a-unary minus, — a+unary plus, + a*multiply, a * b/divide, a / b%modulo, a % b+add, a + b-subtract, a — b<<shift left, left operand is shifted left by right operand bits>>shift right, left operand is shifted right by right operand bits<less than, result is true or false, a %lt; b<=less than or](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*G4pUq67UDWJSZsULGe7j2g.png)
Basic Data Structures
List
- List is a collection which is ordered and changeable. Allows duplicate members.
- Lists are created using square brackets:
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
- List items are ordered, changeable, and allow duplicate values.
-
List items are indexed, the first item has index
[0], the second item has index[1]etc. - The list is changeable, meaning that we can change, add, and remove items in a list after it has been created.
-
To determine how many items a list has, use the
len()function. - A list can contain different data types:
list1 = ["abc", 34, True, 40, "male"]
- It is also possible to use the list() constructor when creating a new list
thislist = list(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # note the double round-brackets
Tuple
- Tuple is a collection which is ordered and unchangeable. Allows duplicate members.
- A tuple is a collection which is ordered and unchangeable.
- Tuples are written with round brackets.
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
- Tuple items are ordered, unchangeable, and allow duplicate values.
-
Tuple items are indexed, the first item has index
[0], the second item has index[1]etc. - When we say that tuples are ordered, it means that the items have a defined order, and that order will not change.
- Tuples are unchangeable, meaning that we cannot change, add or remove items after the tuple has been created.
- Since tuple are indexed, tuples can have items with the same value:
- Tuples allow duplicate values:
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry", "apple", "cherry")
-
To determine how many items a tuple has, use the
len()function:
thistuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(len(thistuple))
- To create a tuple with only one item, you have to add a comma after the item, otherwise Python will not recognize it as a tuple.
thistuple = ("apple",)
print(type(thistuple))
#NOT a tuple
thistuple = ("apple")
print(type(thistuple))
- It is also possible to use the tuple() constructor to make a tuple.
thistuple = tuple(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # note the double round-brackets
print(thistuple)
Set
- Set is a collection which is unordered and unindexed. No duplicate members.
- A set is a collection which is both unordered and unindexed.
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
- Set items are unordered, unchangeable, and do not allow duplicate values.
- Unordered means that the items in a set do not have a defined order.
- Set items can appear in a different order every time you use them, and cannot be referred to by index or key.
- Sets are unchangeable, meaning that we cannot change the items after the set has been created.
- Duplicate values will be ignored.
-
To determine how many items a set has, use the
len()method.
thisset = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print(len(thisset))
- Set items can be of any data type:
set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
set2 = {1, 5, 7, 9, 3}
set3 = {True, False, False}
set4 = {"abc", 34, True, 40, "male"}
-
It is also possible to use the
set()constructor to make a set.
thisset = set(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) # note the double round-brackets
Dictionary
- Dictionary is a collection which is unordered and changeable. No duplicate members.
- Dictionaries are used to store data values in key:value pairs.
- Dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and have keys and values:
thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
- Dictionary items are presented in key:value pairs, and can be referred to by using the key name.
thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
print(thisdict["brand"])
- Dictionaries are changeable, meaning that we can change, add or remove items after the dictionary has been created.
- Dictionaries cannot have two items with the same key.
- Duplicate values will overwrite existing values.
-
To determine how many items a dictionary has, use the
len()function.
print(len(thisdict))
- The values in dictionary items can be of any data type
thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"electric": False,
"year": 1964,
"colors": ["red", "white", "blue"]
}
Conditional branching
if condition:
pass
elif condition2:
pass
else:
pass
Loops
Python has two primitive loop commands:
- while loops
- for loops
While loop
-
With the
whileloop we can execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true. - Example: Print i as long as i is less than 6
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
- The while loop requires relevant variables to be ready, in this example we need to define an indexing variable, i, which we set to 1.
-
With the
breakstatement we can stop the loop even if the while condition is true - With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration, and continue with the next.
- With the else statement we can run a block of code once when the condition no longer is true.
For loop
- A for loop is used for iterating over a sequence (that is either a list, a tuple, a dictionary, a set, or a string).
- This is less like the for keyword in other programming languages, and works more like an iterator method as found in other object-orientated programming languages.
- With the for loop we can execute a set of statements, once for each item in a list, tuple, set etc.
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)
- The for loop does not require an indexing variable to set beforehand.
- To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the range() function.
- The range() function returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 by default, and increments by 1 (by default), and ends at a specified number.
- The range() function defaults to increment the sequence by 1, however it is possible to specify the increment value by adding a third parameter: range(2, 30, 3).
-
The else keyword in a for loop specifies a block of code to be
executed when the loop is finished.
A nested loop is a loop inside a loop. - The “inner loop” will be executed one time for each iteration of the “outer loop”:
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in adj:
for y in fruits:
print(x, y)
- for loops cannot be empty, but if you for some reason have a for loop with no content, put in the pass statement to avoid getting an error.
for x in [0, 1, 2]:
pass
Function definition
def function_name():
return
Function call
function_name()
- We need not to specify the return type of the function.
-
Functions by default return
None - We can return any datatype.


JavaScript:


TypeScript:


React:


Node:

JQuery:

Markdown:

JSON:


Comments
Post a Comment
Share your thoughts!